【study】Spring学习part04
反射
通过Class文件获取到对象相关的内容,并使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
| import org.example.reflect.Car;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class TestCar {
@Test
public void testCarClass1() throws Exception {
Class clazz1 = Car.class;
Class clazz2 = new Car().getClass();
Class clazz3 = Class.forName("org.example.reflect.Car");
System.out.println(clazz1);
System.out.println(clazz2);
System.out.println(clazz3);
Car car1 = (Car) clazz3.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
System.out.println(car1);
}
@Test
public void testCarClass2() throws Exception {
Class<Car> clazz = Car.class;
Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> c : constructors) {
System.out.println("方法名称: " + c.getName() + "\t参数个数:" + c.getParameterCount());
}
Constructor<Car> constructor1 = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class, String.class);
Car car = constructor1.newInstance("问界", 10, "黑色");
System.out.println(car);
Constructor<Car> declaredConstructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Car car1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance("智界");
System.out.println(car1);
}
@Test
public void testCarClass3() throws Exception {
Class<Car> carClass = Car.class;
Field[] fields = carClass.getFields();
System.out.println("public属性有");
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("private属性有");
Field[] declaredFields = carClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(f);
}
Class clazz = Car.class;
Car car = (Car) clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
for (Field f : declaredFields) {
if (f.getName().equals("name")) {
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(car, "问界M9");
}
System.out.println(f.getName());
System.out.println(car);
}
}
@Test
public void testCarClass4() throws Exception {
Car car = new Car("问界M7", 3, "蓝色");
Class<? extends Car> clazz = car.getClass();
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
if (m.getName().equals("toString")) {
String invoke = (String) m.invoke(car);
System.out.println("toString执行: " + invoke);
}
}
Method[] methodAll = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : methodAll) {
if (m.getName().equals("run")) {
m.setAccessible(true);
m.invoke(car);
}
}
}
}
|
手写IoC
实现Spring的IoC过程
1. 创建新的子模块myspring
2. 创建测试类service、dao
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
package org.example.dao;
public interface UserDao {
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
package org.example.dao.impl;
import org.example.dao.UserDao;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
package org.example.service;
public interface UserService {
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package org.example.service.impl;
import org.example.dao.UserDao;
import org.example.service.UserService;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
}
|
3. 创建两个注解
3.1 @Bean创建对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
package org.example.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Bean {
}
|
3.2 @Di属性注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
package org.example.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Di {
}
|
4. 创建bean容器接口ApplicationContext定义方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
package org.example.bean;
public interface ApplicationContext {
Object getBean(Class clazz);
}
|
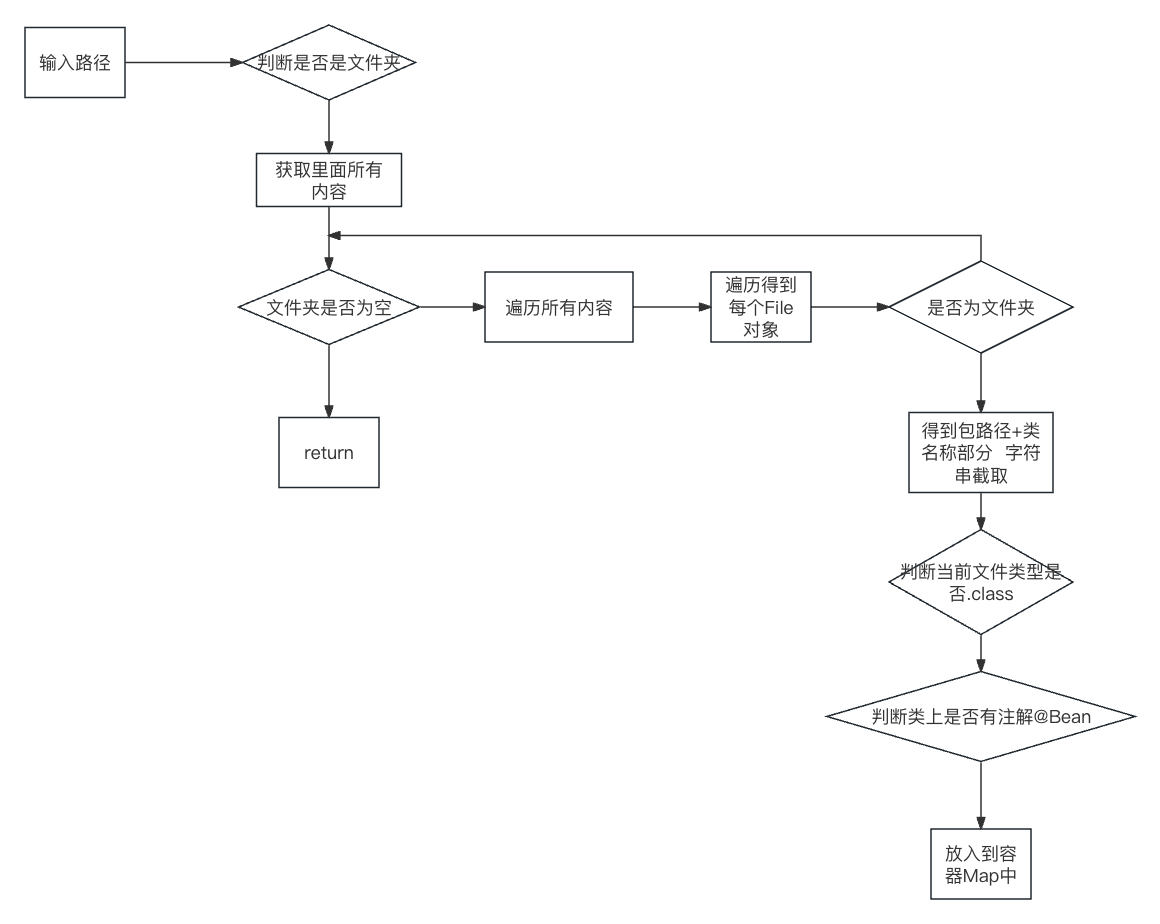
5.实现bean容器接口
- 返回对象
- 根据包规则加载bean
比如org.example,扫描这个包与子包里面的所有类,是否有@Bean注解,如果有则把这个类通过反射进行实例化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
package org.example.bean;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AnnotationApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{
private Map<Class, Object> beanFactory = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public Object getBean(Class clazz) {
return beanFactory.get(clazz);
}
public AnnotationApplicationContext(String basePackage) {
}
}
|